abdomen
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL)
January 4th, 2021
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) is a heterogeneous group of diseases that accounts for 90% of lymphoma diagnoses, with the other 10% being Hodgkin lymphoma (HL).
The most common risk factor for development of NHL is altered immune function, including autoimmune conditions, congenital immunodeficiency diseases, organ transplantation, and immunomodulatory infections. Lymphomas can spread both via the lymph system and hematogenously to all organs in the body, for example to the bone marrow and central nervous system. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma can affect any organ, and consequently symptoms at presentation may be varied and nonspecific. Tissue sampling is required to make the diagnosis of NHL. Excisional biopsy is preferred, although core biopsy may be sufficient.
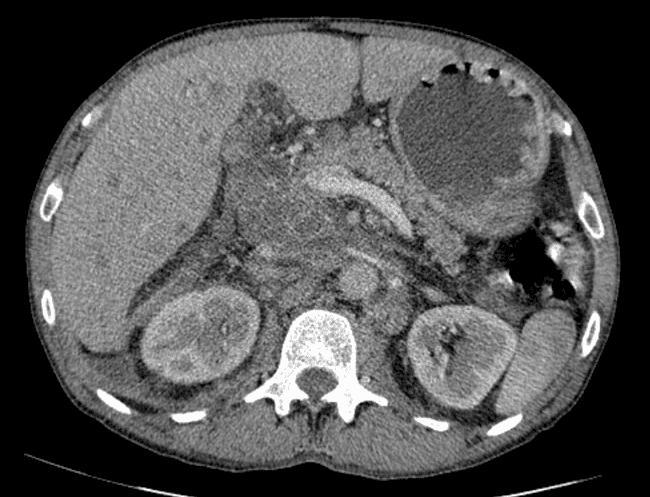
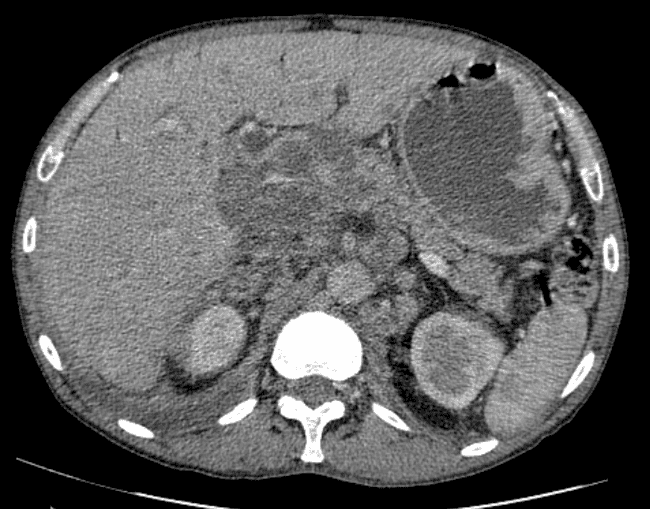
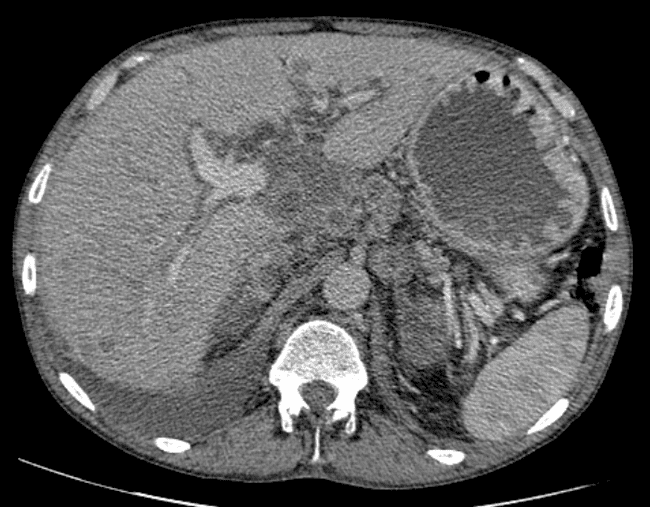
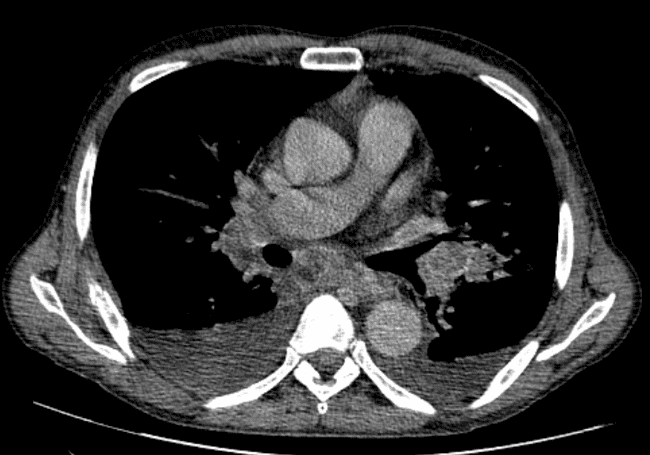
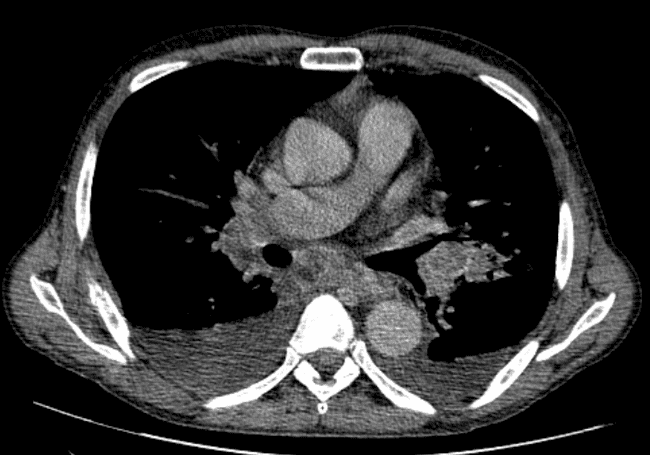
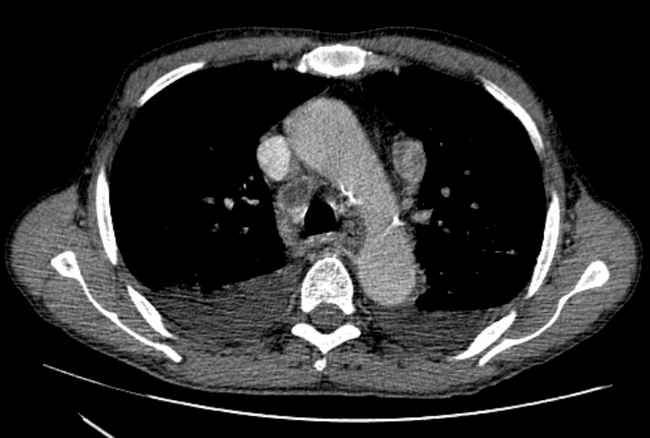
all casesCT: A large conglomerate of periaortic, aortocaval lymph nodes and retroperitoneal necrotic mass which encases the abdominal vasculature. Perihilar and mediastinal lymph nodes, liver metastases. bilateral pleural effusion.